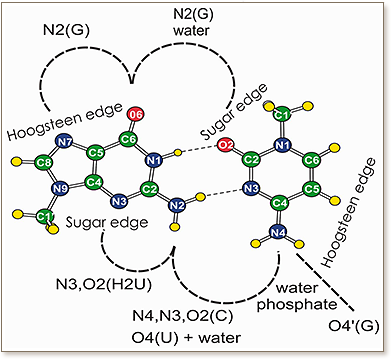
The G:C reverse Watson–Crick (W:W trans) base pair, also known as Levitt base pair in the context of tRNAs, is a structurally and functionally important base pair that contributes to tertiary interactions joining distant domains in functional RNA molecules and also participates in metabolite binding in riboswitches. We previously indicated that the isolated G:C W:W trans base pair is a rather unstable geometry, and that dicationic metal binding to the Guanine base or posttranscriptional modification of the Guanine can increase its stability. Herein, we extend our survey and report on other H-bonding interactions that can increase the stability of this base pair. To this aim, we performed a bioinformatics search of the PDB to locate all the occurencies of G:C trans base pairs. Interestingly, 66% of the G:C trans base pairs in the PDB are engaged in additional H-bonding interactions with other bases, the RNA backbone or structured water molecules. High level quantum mechanical calculations on a data set of representative crystal structures were performed to shed light on the structural stability and energetics of the various crystallographic motifs. This analysis was extended to the binding of the preQ1 metabolite to a preQ1-II riboswitch.